News Center
Multi-sensor complements the advantages of unmanned vehicles
- Categories:Industry information
- Time of issue:2016-12-16 17:26
(Summary description) Today, self-driving vehicles are no longer regarded as science fiction, but as revolutionary technological products that will be realized now! The main reason is that, with the advent of advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) systems and the promotion and development of unmanned driving, cars need to know their surroundings well. The driver can perceive the environment around us, make judgments at the same time, and react quickly in different situations. However, no one is perfect, we will be tired, distracted, and make mistakes due to mistakes. In order to improve safety, automakers are designing ADAS solutions for passenger cars. Automobiles rely on a variety of sensors to sense the complex surrounding environment in different situations. Then, these data will be transmitted to high-precision processors such as TITDA2x, and finally used for automatic emergency braking (AEB), lane departure warning (LDW) and blind spot monitoring functions. There are mainly the following types of sensors used to sense the surrounding environment in autonomous driving technology. Passive sensors-mainly used to sense rays reflected or emitted from objects. Visual image sensor-all imagers operate in the visible spectrum Infrared image sensor-operating outside the visible spectrum. It can be near infrared or thermal infrared (far infrared). Passive sensors are affected by the environment-at different times, weather, etc. For example, visual sensors are affected by the amount of visible light at different times of the day. Active sensor-by emitting rays and measuring the response of the reflected signal. The advantage is that the measurement results can be obtained at any time, regardless of time or season. Radar-by emitting radio waves, the distance, direction and speed of the object are determined based on the radio waves reflected from the object Ultrasound-by emitting ultrasonic waves, the distance of the object is determined according to the ultrasonic waves reflected from the object Lidar-Determine the distance of an object by scanning the laser light reflected from an object Time of flight-use the camera to measure the time taken for the infrared beam to bounce from the object to the sensor to determine the distance of the object Structured light-Project a known light pattern onto an object, for example by TI's Digital Light Processing (DLP) equipment. Subsequently, the camera will capture the deformed light map and analyze it to determine the distance of the object. In order to provide enhanced accuracy, reliability, and durability in a variety of different situations, it is usually necessary to use at least one sensor to observe the same scene. All sensor technologies have their inherent limitations and advantages. Different sensor technologies can be combined to fuse data from different sensors in the same scene, thereby providing a more stable and durable solution, which compares view confusion through data fusion. A typical example is the combination of visible light sensor and radar. Dismantling autonomous driving technology Gill Pratt, head of Toyota Research Institute, listed several technologies related to unmanned vehicles. The first is the smartphone, and its related technologies, low-voltage computer processors, computer vision chips and photographic lenses have become "incredibly cheap and popular." Moreover, cars have shifted from the power plant as the center to the computer as the center. For example, they are equipped with driving recorders, front and rear sensors, and other technologies to avoid hitting objects and warn driving. In addition, the map data system used to identify locations and guide directions, whether it is GPS positioning or Google Map, has become more and more accurate. Deep learning has brought computer perception capabilities closer and closer to humans, allowing unmanned vehicles to recognize the difference between bicycles and pedestrians, signs and trees. Gill Pratt pointed out that the annual "ImageNet Image Recognition Contest" will test the accuracy of using deep learning algorithms to recognize pictures and images. A few years ago, the error rate was as high as 30%, but last year, the error rate has dropped to less than 5%. These key sensing technologies and computing capabilities form the basis for the realization of unmanned vehicles, and most of them overlap with the technologies used in ADAS (Advanced Driver Assistance System). How do self-driving cars see the world Why do you need so many kinds of sensors? Complementary advantages and disadvantages At present, most automakers are equipped with "autopilot" functions in mass-produced vehicles, including Tesla, Volvo, Mercedes-Benz, Audi, etc., in fact, they are equipped with ADAS. If NHTSA's level of autonomous driving is used, most of them are in the first place. Second to third level. However, Google, Ford and Baidu hope to ski
Multi-sensor complements the advantages of unmanned vehicles
(Summary description) Today, self-driving vehicles are no longer regarded as science fiction, but as revolutionary technological products that will be realized now! The main reason is that, with the advent of advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) systems and the promotion and development of unmanned driving, cars need to know their surroundings well. The driver can perceive the environment around us, make judgments at the same time, and react quickly in different situations. However, no one is perfect, we will be tired, distracted, and make mistakes due to mistakes. In order to improve safety, automakers are designing ADAS solutions for passenger cars. Automobiles rely on a variety of sensors to sense the complex surrounding environment in different situations. Then, these data will be transmitted to high-precision processors such as TITDA2x, and finally used for automatic emergency braking (AEB), lane departure warning (LDW) and blind spot monitoring functions.
There are mainly the following types of sensors used to sense the surrounding environment in autonomous driving technology.
Passive sensors-mainly used to sense rays reflected or emitted from objects.
Visual image sensor-all imagers operate in the visible spectrum
Infrared image sensor-operating outside the visible spectrum. It can be near infrared or thermal infrared (far infrared).
Passive sensors are affected by the environment-at different times, weather, etc. For example, visual sensors are affected by the amount of visible light at different times of the day.
Active sensor-by emitting rays and measuring the response of the reflected signal. The advantage is that the measurement results can be obtained at any time, regardless of time or season.
Radar-by emitting radio waves, the distance, direction and speed of the object are determined based on the radio waves reflected from the object
Ultrasound-by emitting ultrasonic waves, the distance of the object is determined according to the ultrasonic waves reflected from the object
Lidar-Determine the distance of an object by scanning the laser light reflected from an object
Time of flight-use the camera to measure the time taken for the infrared beam to bounce from the object to the sensor to determine the distance of the object
Structured light-Project a known light pattern onto an object, for example by TI's Digital Light Processing (DLP) equipment. Subsequently, the camera will capture the deformed light map and analyze it to determine the distance of the object.
In order to provide enhanced accuracy, reliability, and durability in a variety of different situations, it is usually necessary to use at least one sensor to observe the same scene. All sensor technologies have their inherent limitations and advantages. Different sensor technologies can be combined to fuse data from different sensors in the same scene, thereby providing a more stable and durable solution, which compares view confusion through data fusion. A typical example is the combination of visible light sensor and radar.
Dismantling autonomous driving technology
Gill Pratt, head of Toyota Research Institute, listed several technologies related to unmanned vehicles. The first is the smartphone, and its related technologies, low-voltage computer processors, computer vision chips and photographic lenses have become "incredibly cheap and popular."
Moreover, cars have shifted from the power plant as the center to the computer as the center. For example, they are equipped with driving recorders, front and rear sensors, and other technologies to avoid hitting objects and warn driving. In addition, the map data system used to identify locations and guide directions, whether it is GPS positioning or Google Map, has become more and more accurate.
Deep learning has brought computer perception capabilities closer and closer to humans, allowing unmanned vehicles to recognize the difference between bicycles and pedestrians, signs and trees. Gill Pratt pointed out that the annual "ImageNet Image Recognition Contest" will test the accuracy of using deep learning algorithms to recognize pictures and images. A few years ago, the error rate was as high as 30%, but last year, the error rate has dropped to less than 5%.
These key sensing technologies and computing capabilities form the basis for the realization of unmanned vehicles, and most of them overlap with the technologies used in ADAS (Advanced Driver Assistance System).
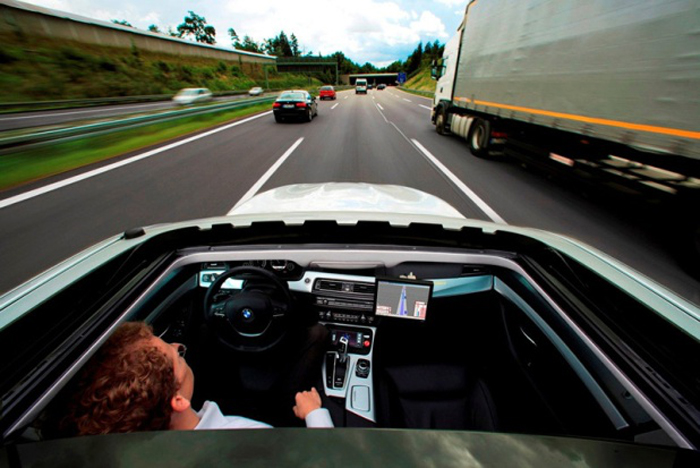
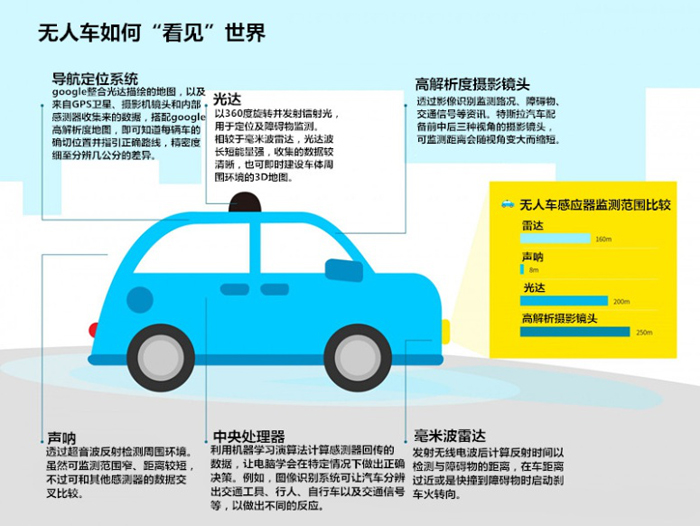
How do self-driving cars see the world
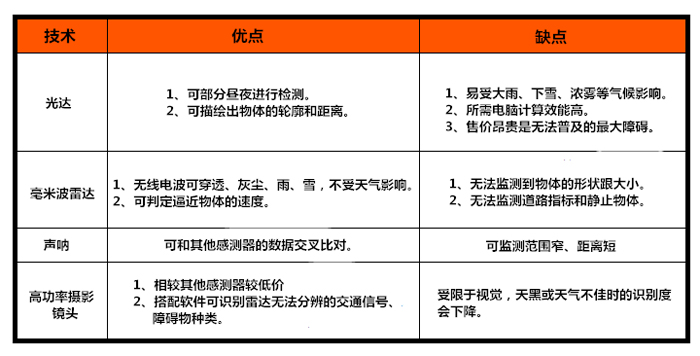
Why do you need so many kinds of sensors? Complementary advantages and disadvantages
At present, most automakers are equipped with "autopilot" functions in mass-produced vehicles, including Tesla, Volvo, Mercedes-Benz, Audi, etc., in fact, they are equipped with ADAS. If NHTSA's level of autonomous driving is used, most of them are in the first place. Second to third level. However, Google, Ford and Baidu hope to ski
- Categories:Industry information
- Time of issue:2016-12-16 17:26






Top Ranking
RECOMMEND NEWS
Top Ranking
RECOMMEND NEWS
ONLINE MESSAGE
WRITE A MESSAGE TO US
v
Contact us
Tel:
+86 731-86171990
Email:
sales@firstratesensor.com
Address: 4th Floor, Building 1, Zhitingyuan, Zhenhua Road, Yuhua District, Changsha City, Hunan Province,China.